Hydroxyproline is a non-essential amino acid that plays a fundamental role in the human body, as it is part of the structure of collagen, the most abundant protein in the human body.
In fact, its presence is so characteristic that hydroxyproline is commonly used as an indirect marker of collagen content in foods and biological matrices. Collagen is essential for maintaining the structure and strength of tissues such as skin, bones, cartilage, tendons, and blood vessels. Hydroxyproline contributes to stabilizing its structure, providing firmness and elasticity.
Why is it important to consume it through the diet?
Although the body can synthesize hydroxyproline from proline, this capacity decreases with age. From the age of 30 - 35 onwards, natural collagen production begins to progressively decline, resulting in loss of skin elasticity, increased joint fragility, and structural aging of tissues.
For this reason, an adequate intake of foods rich in collagen and hydroxyproline becomes especially important in adulthood and during periods of increased physical wear, such as in athletes or individuals with high joint load.
Which foods contain the highest amounts of hydroxyproline?
Hydroxyproline is mainly found in animal-derived foods rich in connective tissue, including:
- Gelatin and gelatin-based products
- Bone broths
- Meat (especially skin, cartilage, and tendons)
- Meat by-products
- Fish and seafood (particularly skin and bones)
These foods provide collagen directly and, consequently, hydroxyproline.
YOUR PLUS: The laboratories of the AGROLAB Group determine hydroxyproline by spectrophotometric quantification of this amino acid after a series of specific chemical steps that allow its proper identification and measurement. This analysis is a key tool for evaluating collagen content in different types of food samples.
Author: Dra. Isabel Gómez, AGROLAB Iberica

 Contact
Contact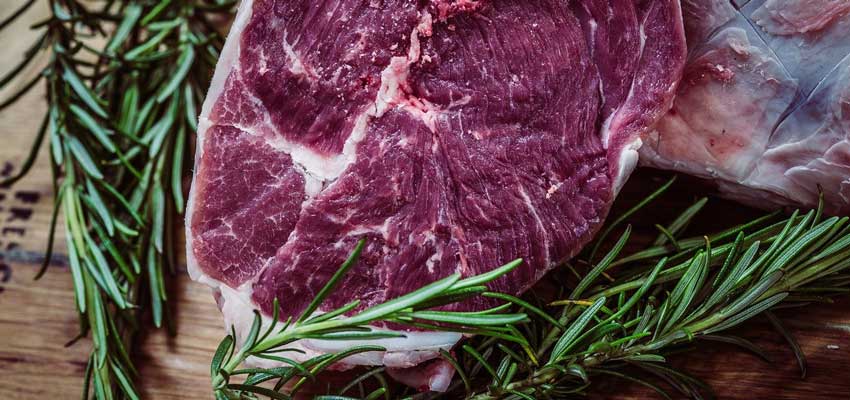

 Contact
Contact Career
Career