Process contaminants are not naturally present in food: The processes of baking, frying, grilling can induce the presence of undeserved substances harmful to human health in food.
What is acrylamide?
Acrylamide is a contaminant according to the definition of Regulation (EEC) no. 315/93 of the European council and, as such, constitutes a chemical danger in the food chain.
It is an organic compound with a low molecular weight, highly soluble in water.
Why acrylamide is present in foods
Often the foods to be eaten must be cooked. The cooking process gives the foods organoleptic and aesthetic characteristics that make them more palatable and tasty. The Maillard reaction is one of the most popular chemical reactions in the world. Chefs, but not only, have long learned that starchy ingredients such as potatoes and cereals, which are not appetizing from raw, can be transformed into toasted delicacies with the addition of heat and a little time.
At high temperatures, above 120° C, the interaction between sugars and amino acids (in particular asparagine) gives these foods their characteristic taste and distinctive color but also has an undesirable effect, which is the production of acrylamide.
The acrylamide will be the more present the higher the sugar and amino acid content.
Legislation
In 2002 it was discovered that when cooked starchy foods lead to the presence of an unwanted contaminant in the food.
In 2012, some countries such as Denmark, France, Germany and Sweden asked EFSA to consider the suspected carcinogenicity of acrylamide for humans. EFSA issues a scientific opinion.
In the following years, other studies were done, especially regarding the exposure of consumers to this "new" process contaminant.
Recommendation 2013/647 / EU on the levels of acrylamide in food
Regulation (EU) 2017/2158 establishing mitigation measures and reference levels for the reduction of the presence of acrylamide in food.
What AGROLAB can do!
AGROLAB provides a complete and accreditated analytical service for the research of acrylamide in all types of food listed in Regulation (EU) 2017/2158. The analytical method, developed internally, presupposes the use of liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) after an extraction phase followed by SPE purification. The laboratory can also support the various subjects of the food chain for an adequate control of the sugar and amino acid content
The technical assistance at the laboratory and your regional sales representative will be happy to provide you with all the information necessary for sampling and interpreting the data obtained in the laboratory.
Author: Giulio Lora

 Contact
Contact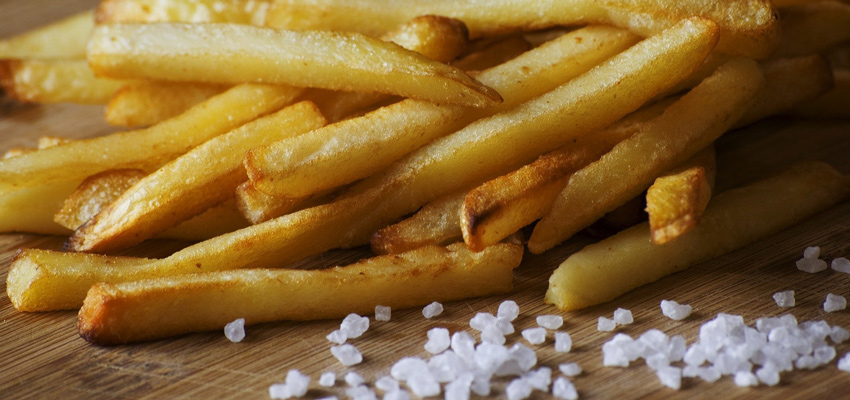

 Contact
Contact Career
Career